Improvements in vision technology are expanding the realm of possibility for factory automation.
If there’s anything we’ve learned from decades of work in the automation industry, it’s that the transformative impact of a new technology reaches beyond its immediate applications. Sometimes, the new technology means that old systems must be reworked to accommodate it. In other areas, the new capabilities resolve old problems, eliminating trouble points and opening new possibilities for manufacturers.
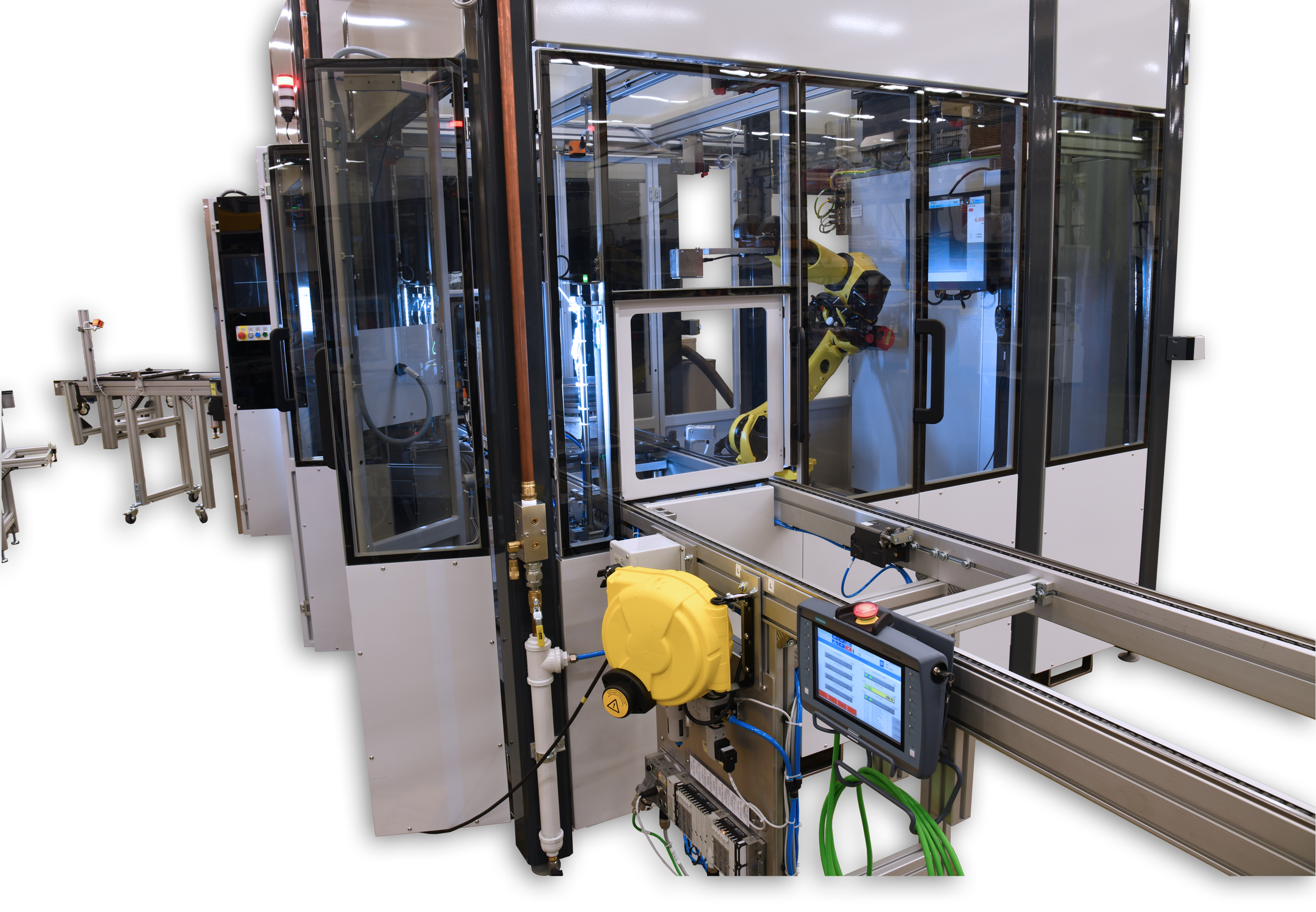
Vision technology is one of the innovations currently pushing the boundaries of factory automation. As computers become more sophisticated in their ability to identify objects and spatial relationships through cameras and other sensors, their reliability, and versatility in practical applications will only expand. Here are four ways where vision technology is currently improving automated manufacturing around the world.
1. Quality control: monitoring production output for flaws.
Production errors can cost manufacturers millions, whether or not they make it to market. Components that don’t pass quality control standards lead to waste, while those that do make it into the hands of consumers can result in damaged consumer trust at best, and huge legal fees.
Because of this many businesses have been willing to invest in quality control measures over the years, some of which are more effective or easier to implement than others. The good news is that vision systems are becoming ever more affordable as quality assurance tools, and are often easier to implement and more versatile than many of their counterparts.
The chief advantage to vision systems is that a single system can detect a range of production flaws. They can also be hooked up to a centralized system, making it easier for operators to check components that have been marked as flawed before those parts make it further into the production stream.
2. Process tracking: inspecting components at each stage of production.
The rise of big data has provided manufacturers with more in-depth production data, allowing them to track automated processes from raw materials to end product—and at every stage of packing and shipping in between. While some of this tracking is enabled by computer chips and ID tags, vision systems also play a key role in monitoring and scanning products along the way.
Vision technology can also be used to monitor systems that are less predictable. For instance, vertical farms can use vision technology to determine when crops are ready to be harvested. While some of these applications may be very specific, they are only possible through the use of this technology.
3. Advanced robotics: enabling responsive programming.
One of the great advantages of using advanced robotics in modern manufacturing settings is that high-end robots are less specialized and therefore more adaptive than their hard-programmed counterparts. Traditionally, an automated machine is designed to perform a single action hundreds of thousands of times a day. However, to achieve this output, parts must be carefully fed into the machine and positioned so that the machine has a consistent environment.
By contrast, advanced robots are able to adjust to their environments, or even be reprogrammed to perform different tasks multiple times a day. The robot doesn’t need a component carefully placed in a uniform position on a conveyor belt if it can “see” each component well enough to pick it up, reorient it, and then apply it to the next stage of automation.
Similarly, a robot moving across a factory floor doesn’t need a track cleared for it so long as it can detect and avoid potential obstacles. The ability of robots to monitor and respond to their environments is quickly making them some of the most valuable assets in the modern manufacturing plant.
4. Worker safety: improving environmental awareness.
As automated systems become more mobile, they are taking over many tasks that are dangerous or physically demanding for human workers. However, this also means that robots are in closer contact with people, often while moving at high speeds or while handling heavy components. This introduces new risks to employees, even as it eliminates old ones.
Fortunately, the very technology that allows robots to move through a changing environment without colliding with anything also provides a means for them to change their behavior when people are present. Vision and advanced sensor technology can be programmed to detect when a human worker is nearby, causing a machine to slow down or come to a stop until the person has passed by.
Vision systems can also be applied to automation stations that are fixed in place, although other solutions, such as light curtains or safety mats, may be more effective.
As technologies improve, new uses become possible. Work with a team that understands the new capabilities through and through.
It’s tempting to view new technological innovations as replacing an old set of problems with a new list of challenges to be overcome. However, most new technologies only introduce new challenges by shifting the bar with regard to what is possible.
For manufacturers who want to use each new technology to its fullest advantage, it’s important to work with an automation provider who understands the implications of these new technologies to their fullest extent. At Eagle, we practice this pursuit of continual improvement as one of our core business philosophies. We are not only looking for new ways to help our clients improve the quality and safety of their manufacturing processes, we also use advanced technology to rethink our own systems. We want to be sure that no stone is left unturned in our search for the best solution for our customers’ needs.
Contact us today if you would like to speak to us about how our automated systems can improve your manufacturing processes.
Brandon Fuller | b.fuller@EagleTechnologies.com
Eagle Technologies, headquarters in Bridgman, MI
Eagle builds the machines that automate manufacturing. From high-tech robotics to advanced product testing capabilities, Eagle offers end-to-end manufacturing solutions for every industry.