The high complexity and low volume of aerospace manufacturing pose challenges to automation. Here’s why the industry still needs it.
For decades, the aerospace industry has been a pioneer in the field of engineering, pushing boundaries and redefining modern life in numerous ways. Yet, for one of the most sophisticated industries in the world, aerospace has faced significant challenges in incorporating factory automation into its production processes.
There are several reasons for this according to the team at Eagle Technologies. Aircraft are not only technologically complex, they’re also enormous in comparison to other “products”, complicating the design of any automated processes. However, the main limiting factor that prevents a more widespread adaption of factory automation is that the production volume for aerospace is significantly lower than in other industries.
For instance, the Boeing 737, which currently holds the record for the highest number of units built, has only produced 10,584 aircraft from 1968 to the present. By contrast, Tesla, still some consider an underdog (not me) in the automotive market, delivered 139,300 units in the 3rd quarter of 2020 alone.
Nonetheless, factory automation has numerous benefits to offer the aerospace industry, and despite the costly up-front investment, the returns in efficiency, quality control, and worker safety make it easy to justify. The key is knowing where to apply it.
1. Robotic systems that can replace large monument assemblies.
As we mentioned before, the size of aerospace assemblies is one of the most significant limiting factors when it comes to automating production. In the past, addressing this issue meant building large assemblies to match, but the increased mobility and sophistication of modern robots offers a new solution.
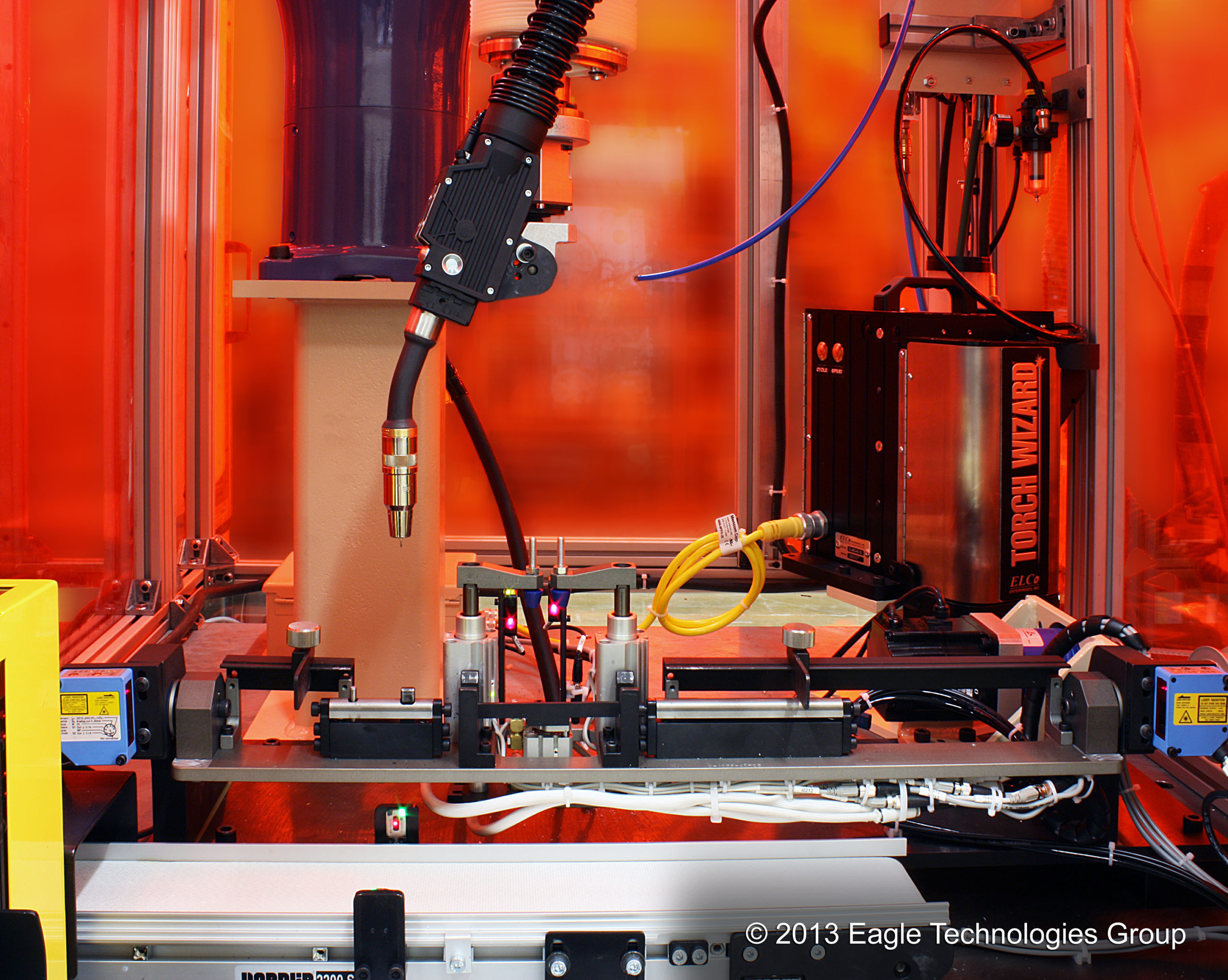
Robots equipped with vision systems can now move around large aerospace assemblies, performing complex tasks that previously would have required human assembly. For instance; Eagle has built equipment that integrates large – heavy payload robots manufactured by Fanuc, Yaskawa, and ABB that move components that weigh hundreds of pounds. They can also perform a greater variety of tasks, rather than one single task.
2. Collaborative robots that operate alongside factory workers.
Some tasks will still require human intervention to perform. This has sometimes made it difficult to design automated systems, because the presence of workers increases the risk of injury.
However, the same advances in vision technology that allow robots to move around an aircraft assembly also make it safer to have them working in the same environment as human workers, leading to a faster production process.
3. Drilling, cutting, riveting, and deburring.
More mobile robots that can work alongside humans is a promising vision, but what tasks can they perform? This is the space where full-factory automated solutions show their true potential.
Learn more about material removal here.
From cutting aerospace parts to fastening them in place, robots provide an automated solution that can expedite some of the larger and more difficult repetitive assembly tasks. Automating the assembly of an entire airplane is a monumental task. But when processes require a specific process to be performed hundreds of times—like drilling holes at designated locations —developing automation to accomplish the task becomes much more feasible.
4. Applying sealants, paints, and coating.
Robots can also be used to apply a range of fluids where necessary. For instance, after riveting parts into place, a robot could apply sealant to the rivet or along a joint in the fuselage. Besides decorative paint, aircraft also require a range of coatings to protect against harsh flying conditions, reduce drag, and improve the efficiency of the aircraft.
Learn more about dispensing here.
The application of these paints and coatings is one that can be handled by automation. Not only can automated systems apply these coatings evenly, they can do so much faster than human operators, allowing the aircraft to spend less time in production.
5. IIoT advancements that improve quality and production flow.
Finally, the advancement of industry automation technologies offers aerospace manufacturers new quality control abilities while also giving them a thorough overview of their production process.
Smart robots can communicate with a centralized control module about the rate of production and the status of each individual robot. They can also use vision technology to scan for flaws and report and abnormalities. In many cases our in-house software package can be deployed to work within your MES system.
Factory automation industry is adapting to deliver an impressive ROI for aerospace manufacturers.
In the early days of factory automation, finding ways to apply high-volume processes to low-volume industries was difficult and met with mixed success. It’s no wonder, therefore, that aerospace manufacturers hesitate to invest in automation that are less certain than in other industries.
At the same time, demand for aircraft is rising at a rate that aerospace manufacturers are struggling to meet. To meet this demand, aerospace manufacturers need to turn their focus toward automated solutions.
Businesses in the aerospace sector work on longer timeframes than in other industries, so while it may take longer for an investment made in an automated system to pay itself off, aerospace manufacturers can expect the automated system to be usable for many years to come. In the meantime, ROI will show itself in other ways.
Automated systems will reduce labor costs at a time when a shortage in skilled labor adds complication to the production process. With less human involvement there is also less risk of injury, leading to a safer working environment. And, of course, automation will mean manufacturers will be able to produce more components of a higher quality and with less cost.
At the end of the day, the conclusion is clear. Aerospace manufacturers who want to maintain their competitive edge must look to factory automation. It’s the only solution that can take their business to new heights and keep up with other industry innovators.
Brandon Fuller | b.fuller@EagleTechnologies.com
Eagle Technologies, headquarters in Bridgman, MI
Eagle builds the machines that automate manufacturing. From high-tech robotics to advanced product testing capabilities, Eagle offers end-to-end manufacturing solutions for every industry.