Taking full advantage of the IIoT isn’t just about WIFI-enabled machines. It’s about full factory connectivity.
Ever since the first cell phone gained Internet access, the word “smart” has been appended to every Internet-enabled device, regardless of its quality or utility. Today, almost every electronic device can be “smart,” from smart home security devices that can let you in even if you forgot your keys, to a smart crock-pot that will let you monitor the progress of dinner from your smartphone. With the “smart” label applied to so many technologies, it can hide the fact that in some cases, Internet-enabled technologies aren’t just a convenience—they’re a game changer.
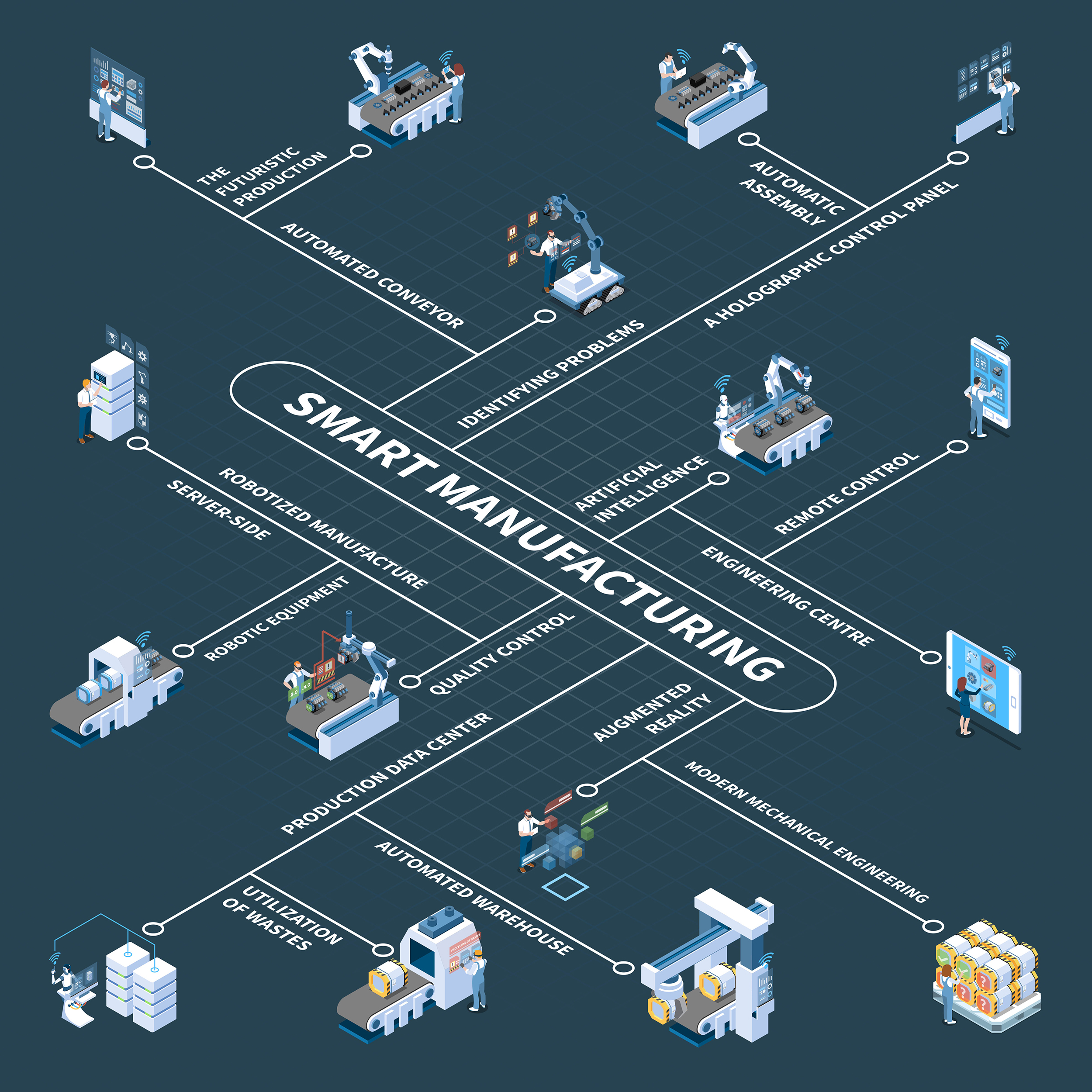
Few places is the impact of this new technology so widely felt as in manufacturing. Internet-enabled machines, which are part of the IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things), are gradually reshaping how factories are designed and operated. And with each innovation, the gap widens between businesses who have been early adapters of this new technology, and those which have lagged behind.
IIoT, at its fullest, isn’t just comprised of devices which are connected to the Internet, but of devices which, through the Internet, are connected to each other. A “smart factory” is one in which the Internet capacities of all devices are interconnected, allowing devices to communicate with each other, respond to their environment, and deliver up-to-the-second data to factory overseers.
The full benefits of smart manufacturing have yet to be fully explored, but here are a few immediate advantages they provide to manufacturing businesses.
1. Identify the source of production errors more quickly.
A production flaw in a component can grind factories to a halt as the manufacturers examines each section of their assembly to find the source of the error. IIoT can expedite this process by delivering the full data set for each component’s production history. Quickly tracking the problem back to its source can prevent businesses from sending a faulty product to market, damaging their credibility as a producer of high-quality goods, and potentially losing millions in recalls and law suits.
2. Update supply chain systems with timely production data.
Supply chains are global, and a competitive business needs to be able to track shipments even after they leave the factory floor. While current technology, such as RFID tags, can help businesses keep an eye on parts, these tracking methods can’t provide the full picture. However, IIoT tracking systems can. They can help businesses monitor the status of new shipments, check in on the progress of items on the factory floor, and trace the distribution of products after assembly.
3. Monitor and adjust system operations remotely or autonomously.
Smart manufacturing factories tend to reduce the number of employees on the floor at any given time. While this can improve employee safety by distancing them from potentially dangerous production processes, it also means that there are fewer eyes physically in the space to oversee operations. On the other hand, it multiplies the number of virtual eyes tracking progress, meaning that an operator stationed in a central monitoring location can spot a problem, such as an impending collision, and take control of the robot remotely. Moving machine components can also be programmed to respond and adapt to each other in a dynamic environment, improving performance across the factory floor.
4. Anticipate and schedule preventative maintenance during down time.
When a machine breaks down unexpectedly, it disrupts the entire supply chain. Downstream processes are left without enough components to progress, while upstream processes continue to deliver raw materials that pile up, unused. The solution to this problem is clear: target potential breakdowns before they happen, and schedule preventative maintenance. IIoT technology can achieve this by using advanced sensing technology to spot variances in a machine’s output that go beyond an acceptable deviation.
5. Relay process data back to the research and development team.
We usually think about R&D teams using simulation, prototyping, and extensive testing to settle upon design standards that the assembly team must then meet. But what if the R&D team could draw upon production data during their design process?
One of the most valuable insights production data can provide lies in how to improve the production process itself. Assembly steps that waste resources, require excessive number of steps, or introduce potential points of error into the production stream should all be avoided. Instead, engineers should look to the production data for ways to streamline assemblies to be more efficient and error-proof.
Contact Eagle to learn more about how to bring the advantages of IIoT to your factory.
At Eagle, we have a long history of identifying and implementing transformative technology. This extends to the IIoT. Our team is more than eager to help your business find new ways to make this technology part of your production process. Our deep experience of over 70 years in the manufacturing industry means we have a wealth of knowledge to draw on as we create an automated assembly that fully incorporates Internet 4.0 capabilities.
Contact us today if you would like to learn more about how our team can help yours.
![]() Connect With Eagle Technologies LinkedIn
Connect With Eagle Technologies LinkedIn
Eagle Technologies, headquarters in Bridgman, MI
Eagle builds the machines that automate manufacturing. From high-tech robotics to advanced product testing capabilities, Eagle offers end-to-end manufacturing solutions for every industry.