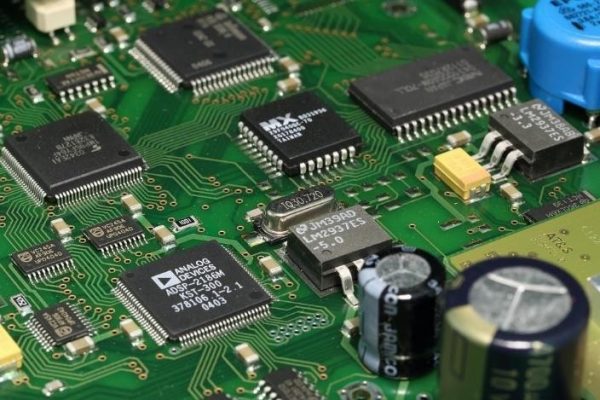
Factory automation accelerates the production of printed circuit boards (PCBs) for high-end electronics.
Electronics come in all shapes and sizes, but one thing almost all of them share is the use of printed circuit boards (PCBs). Circuit boards are a compact and repeatable way to structure intricate components into a small space, making them integral to modern computing. And with more and more devices coming equipped with computer chips such as the Electric Vehicle industry, production of PCBs is only going to continue to rise.
As technology has advanced, these components have grown both smaller and more sophisticated, therefore necessitating the use of automated systems in their production process. Factory automation in PCB production enables higher production outputs, more complex, advanced components, and more reliability and quality control. Furthermore, automated assemblies are only growing more efficient, as they are aided by simulation technologies that can help plan PCB circuit layouts.
As a process that has fully embraced automation, PCBs provide a useful showcase for the capabilities of factory automation in industries that are seeking solutions to their own needs. Here are seven ways PCB manufacturing applies automation technology to streamline production processes.
1. Loading and positioning of components throughout the process.
Circuit board components aren’t just small; they’re also fragile. Careful handling of each piece is required to make sure nothing breaks or is damaged in the production process. Furthermore, each piece must be carefully set in place so that every component is properly aligned. On larger systems like wire bonding technologies in the EV industry, Eagle will integrate multi-axis servo systems to present the customer parts to the bonding technology using vision systems.
Modern robotic technology offers fine-tuned material handling capabilities that can lift, orient, and place components in just the right position for each production stage.
2. Application of soldering paste.
Before components can be positioned on a circuit board, soldering paste must first be applied to the correct areas of the board. This is done by placing a stencil on the circuit board, and then spraying or rolling soldering paste onto the surface.
Automated application technology can carefully control the volume and direction of soldering applications so those excess materials aren’t wasted.
3. Automated mounting and wiring of components.
The task that requires the most precision is that of laying down wiring and plugging various computing components into place. Many of these components are extremely small, and as each circuit board requires a significant number of components, placing them by hand would be a laborious endeavor.
Fortunately, automation saves the day. Each circuit board can be positioned underneath a machine that is programmed to apply circuitry and other components at a rate of ten or twenty per second, without the risk of human error.
4. Testing of circuit board wiring and functionality.
Given the complexity required in assembly, testing PCBs at the end of the assembly is essential to guarantee product quality. For the first step, PCBs are checked to be sure that there are no improperly placed circuits that might prevent a PCB from properly transmitting energy. The second testing step involves using highly technical software to verify that the PCB is working appropriately. Each of these steps requires advanced testing capabilities, which we incorporate into all our assemblies as needed.
5. Miniaturization of components.
Each time a PCB gets smaller, it enables the development of tinier and tinier components. This miniaturization can only be attained with the aid of factory automation. Today’s most advanced automated systems can apply adhesives and lubricants at microscopic levels, allowing for assemblies of similarly microscopic proportions.
6. Tracing of PCBs throughout the production process.
Apart from assembling components, factory automation can also be used to keep track of them as they move along the production line. In automated product tracing, a bar code or other tracking device is applied to the component, which is then scanned at each checkpoint. These tracking codes help businesses monitor production speed, look for inefficiencies in the process, and pinpoint any production flaws that may occur.
7. Packaging of PCBs.
Finally, with such a high volume of fragile products, businesses need to be able to package them safely for transport and delivery. Automated packaging can wrap, stack, and palletize completed PCBs so that they aren’t damaged on the way to their final destination.
Eagle is ready to serve all your factory automation needs.
As leaders in the factory automation industry for nearly seventy years, we’ve seen our share of new technologies revolutionizing industries. Our favorite challenges come when we take these technologies and develop automated solutions that are more efficient and reliable than previous solutions. And we are always on the lookout for innovative ways to get the job done, be it Industry 4.0 simulation technology that lets us model our assembly methods or advanced monitoring systems that let us trace components through the production line.
If you have an automated assembly need for your business, we encourage you to call us today. Tell us about your need, and we’ll tell you about our solution.
.
Brandon Fuller | b.fuller@EagleTechnologies.com
Eagle Technologies, headquarters in Bridgman, MI
Eagle builds the machines that automate manufacturing. From high-tech robotics to advanced product testing capabilities, Eagle offers end-to-end manufacturing solutions for every industry.