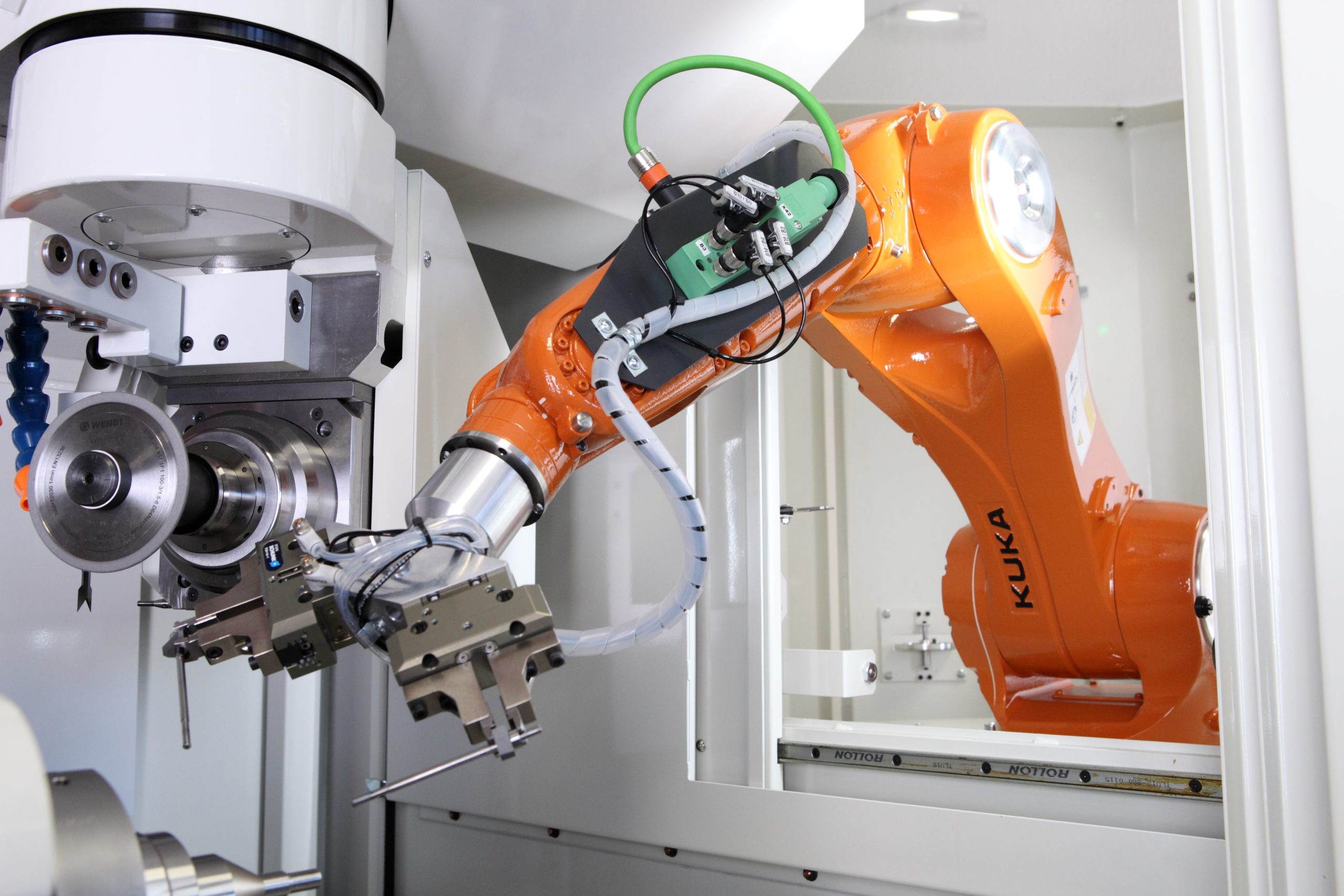
One of the most widely-used metal forming processes can be made even more efficient with automation.
Die casting is a popular process for good reason. It produces castings quickly and consistently, with a high level of precision, and can minimize the amount of post-processing needed for the final product. The dies themselves, as well as the injection and processing equipment, represent a significant capital investment up-front—but for high-volume production, the efficiency gains are a clear win. Processes that hinge on this kind of precision and repeatability are excellent candidates for automation—in these cases, automated systems can act as a multiplier, creating efficiency gains at every step.
Additionally, die casting involves high temperatures, pressurized molten metal, and other potentially dangerous materials that can represent a risk to worker safety. Introducing robots that can tolerate such conditions helps create safer and more comfortable work environments for human operators, and delays wear and tear on existing equipment.
Automation is one key option for increasing the throughput, safety, and quality of the die casting process. Here are four areas where it can have a sizable impact.
1. Faster handling, safely.
Worker safety is the highest priority in any manufacturing setting. In die casting, high temperatures and pressures mean that safety procedures are crucial, and that speeding up production involves plenty of additional considerations to protect life and limb.
Robotic equipment, however, offers additional flexibility when designing workflows for ladling or injecting, ejecting molds, or positioning and gripping die halves. Automated systems can be designed with temperature-resistant and protective surfaces that can tolerate the harsh requirements of working with molten metal. These automated processes offer the opportunity to increase the efficiency and throughput of existing processes, while maintaining—and even enhancing—worker safety.
2. Machines tending machines.
Before casting, dies need to be lubricated, to ease the removal of the finished product. This lubrication must be done precisely and consistently, otherwise the casting might develop flaws during cooling or ejection. Automated dispensing technology can carefully control the lubrication process, ensuring a consistent amount of lubricant, evenly applied.
However, the lubricant—and other fluids involved in the casting process—present their own problems. Material removal during post-processing creates dust and metal shards, which, when combined with casting fluids, produces an abrasive sludge that can cause wear and tear on the moving parts of existing equipment.
But the consistency and precision of an automated casting process can reduce the amount of post-processing needed on each individual casting, making the removal of flashing, sprues, and other waste more efficient and contained. That leaves fewer scraps to contribute to abrasion, increasing the longevity of the system as a whole.
3. Visual inspection and quality control.
One of the greatest advantages of the die casting process is its repeatability. But even with the consistency of the finished product, inspecting each piece after it has been ejected and cooled is critical—particularly considering die casting’s use in industries with tight tolerances for variation, like automotive and aerospace. Slight surface defects or minor internal flaws can result in serious downstream safety risks or major equipment failures.
Fortunately, automated inspection processes are becoming more accurate every day, thanks to an array of technological improvements. Vision systems are more sophisticated and flexible, with access to a variety of measurement tools and large training datasets. These and other high-tech metrology systems that verify the fine details of a product’s shape, or detect production flaws using sensors and techniques inaccessible to human workers, can be incorporated smoothly into an automation workflow. Material handling and conveyance systems can then use the information provided to sort out and remove any imperfect products efficiently.
4. Reduced waste, reduced cost.
Robotic equipment can accomplish dangerous or intricate jobs precisely and without declining in quality over time. These characteristics alone mean a higher success rate on products, with less rework and fewer rejected pieces. But on top of that, the ability of robots to work in ways that human operators can’t means that automated systems have additional flexibility when positioning dies, injecting alloys, ejecting hot castings, or completing any necessary post-processing. Automated systems can handle these tasks efficiently and with a consistently high-quality output.
Robotic material handling also means that dies can be designed to minimize the occurrence of sprues, flashing, and other post-processing concerns. A robotic arm can access tight areas for drilling or deburring, and can handle extremely precise material removal with a minimal risk of errors. With their emphasis on repeatability, the results of automated systems—including waste—are much more predictable. Processes can be designed to control their own dust, metal scraps, and other byproducts, which can be disposed of safely or reclaimed for other uses.
Die castings’ biggest hurdles are where automation shines.
Die casting involves detailed, precise tasks done under conditions potentially dangerous to workers. Ladling hot metal, handling hot dies and castings, and post-processing castings amid metal scrap all carry the potential for injury, to say nothing of product waste if the processes aren’t completed correctly. The repeatability of these tasks make them excellent candidates for automation by equipment that’s been designed to handle the harsh operating environment.
Eagle Technologies specializes in creating automated systems that include a wide variety of material handling technologies. We work with specialized solutions like dial machines and hitch feeds, as well as more traditional options like conveyor belts. Our expertise also covers material removal technologies, from deburring and laser ablation to plasma cleaning, designed to suit your specific needs. If your metal forming business is ready to take the next step in safety and efficiency, contact Eagle today. We can help you find the right automation solution for your factory floor.
![]() Connect With Eagle Technologies LinkedIn
Connect With Eagle Technologies LinkedIn
Eagle Technologies, headquarters in Bridgman, MI
Eagle builds the machines that automate manufacturing. From high-tech robotics to advanced product testing capabilities, Eagle offers end-to-end manufacturing solutions for every industry.